Porcelain replacement money
Before the outbreak of World War I, the German economy began to feel the effects of the population's panic hoarding of metallic currency. First, gold 10 and 20 markov coins began to disappear from the market, then silver coins, and finally there was a shortage of small copper, nickel and iron money. The solution to this situation was to be the launch of private issues of various types of vouchers to facilitate mutual settlements between people. In 1914, the first vouchers (notgelds) appeared, usually containing only the denomination, a stamp and a signature, or possibly the name of the town, on a piece of paper.
Over time, however, their production reached the technical level of normal banknotes - but generally they were to be distinguished by, for example, smaller size, shape, or the material used (colored paper, textile material, cardboard, etc.). Tens of thousands of such banknotes are known and catalogued. In addition to the vouchers, substitute coins were minted in parallel, made of iron, zinc, aluminum, brass, copper, nickel, cardboard, often with very strange shapes - oval, square, wavy, octagonal, with holes cut out, etc. It sometimes happened that graphically attractive issues ended up in the hands of collectors immediately after their release.
In the 1920s, one of the unusual materials for the production of coins was
porcelain. Not for the first time - see Chinese and Siamese porcelain coins.
porcelain coins, despite sometimes large expenditures, did not circulate in
normal monetary circulation - but were eagerly collected by the population.
Thanks to the adventurous alchemist Johann Friedrich Böttger in 1709, the
Chinese monopoly on porcelain production was broken in the workshop of Walter
von Tschirnhaus.

Instead of gold, Böttger, a subject of Augustus II the Strong,
brought his ruler considerable income from the porcelain production technology
he invented. A year after the discovery, the first porcelain factory in Meissen
began operating dynamically. https://tramp.travel.pl/publikacja.php?p=id34strona1/
There are two types of porcelain:
hard with a composition of 40-60% kaolin, 20-30% quartz, 20-30% feldspar (part
of the kaolin can be replaced with white-fired clay)
soft with a composition of 25-40% kaolin, 30-45% quartz, 25-40% feldspar
Unglazed porcelain, the so-called bisque - firing temperature 920 - 980 degrees
C
Glazed porcelain - firing temperature 1280-1460 degrees C
porcelain coins were made of plaster and steel stamps. Virtually all proof coins
and medals up to 100 pieces come from plaster stamps:
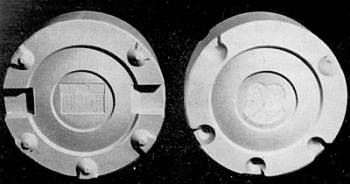
For larger quantities, steel stamps were engraved:

The prepared clay mixture is placed in plaster stamps by
injection or by pouring it into plaster molds. The formed coin is dried for 2
weeks at a temperature of 60 degrees. Then, dried, it is fired at a temperature
of approximately 1,200 degrees for 24 hours. The coin loses about 1/6 of its
volume in this way. After cooling, it is ground and polished. The brown bisque
is lightly oiled. Some coins and medals are additionally decorated with gold,
silver edges and relief. Sometimes the edges were dyed black or green. Each coin
was painted by hand. Such decorations were subjected to additional heat
treatment at a temperature of about 800 degrees.
Typical porcelain coins from brown and white porcelain with decorations shows a
photo of 10 branded coins of the city of Meissen:


Coins made from plaster stamps are usually much thinner than coins made from steel stamps. They also have blurry lettering that often reaches to the very edge of the coins.
In addition to porcelain, clay coins were also produced (including Bolesławiec - Bunzlau)

and majolica - the equivalent of faience. On the 100 mark coin from the city of Waiblingen the famous "Redbeard" - Frederick Barbarossa and on the coin from Ravensburg Prince Henry the Lion and the blackened one from Gaildorf

An interesting fact are coins from the city of Gotha with a high quartz content, popularly called "quartz" - they are characterized by high brittleness and therefore it is difficult to obtain pieces of these coins without chipping.

Graphite was also an interesting and unusual material for coin production:
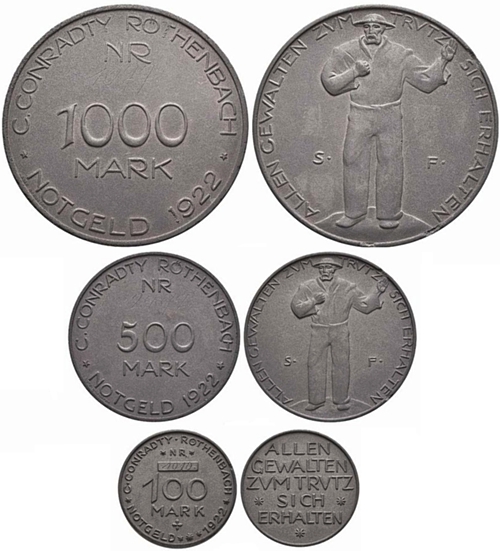

Graphite coins from the Bavarian city of Röthenbach - Photo: Sincona73/2021/250CHF
COMPANIES PRODUCING PORCELAIN AND CLAY COINS:
1. Staatliche porcelain Manufactory Meissen
2. Meissner Ofen- and porcelain factory (C.Teichert)
3. j.w. filia w Bitterfeld
4. Bunzlauer ceramic workshops Reinhold & Co.
5. Deutsche diameter & Steinwerzeuge A.G. in Charlottenburg
6. Brickworks III w Elmschenhagen
7. Freiberger porcelain factory
8. Töpferzentrale in Höhr (Westerwald)
9. Wächtersbacher Steingutfabrik w Schlierbach
10. Krister porcelain Manufactory AG in Waldenburg
11. porcelain factory in Ludwigsburg
12. porcelain factory in Stadt Lengsfeld
13. porcelain factory Pfeffer in Gotha
14. Majolika- Werke in Gaildorf
